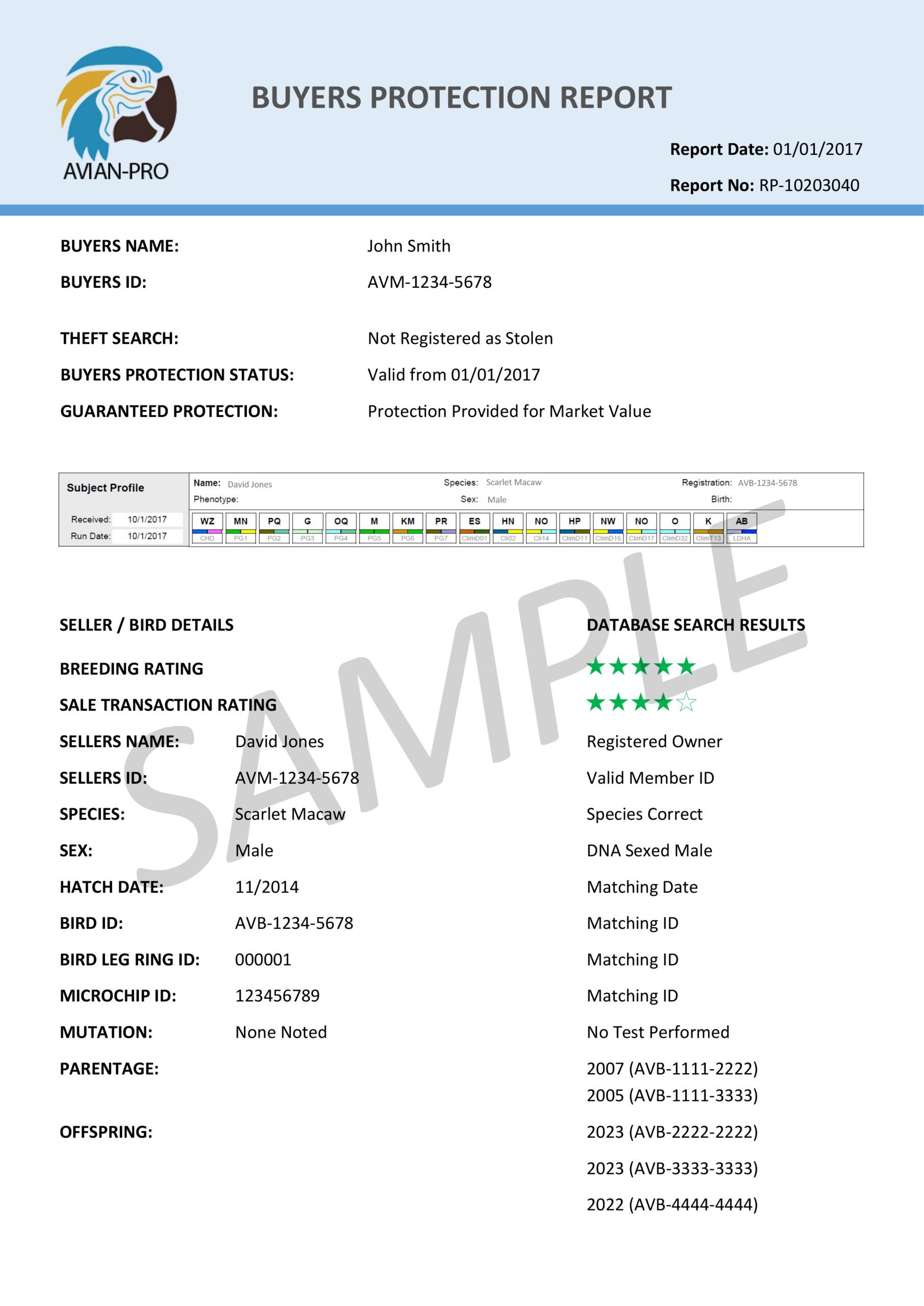
Nutri-Max – All Organic Pre-Breeding Conditioner.
Nutri-Max™ is a premium, all-organic supplement designed to support breeding parrots through every stage of reproduction by harnessing the extraordinary nutritional power of bee pollen—nature’s most complete food. Carefully formulated using lotus flower & sunflower bee pollen to nourish and activate the hypothalamus–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis, Nutri-Max delivers bioavailable nutrients and natural growth factors that stimulate reproductive function, enhance fertility, and improve the health and vitality of both breeding pairs and their chicks. With over 250 biologically active compounds, bee pollen offers a rich matrix of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, antioxidants, enzymes, and phytonutrients that work synergistically to boost energy, immunity, hormone regulation, and egg viability—making Nutri-Max the ideal foundation for a successful breeding season.
✅ Supports Natural Hormonal Balance with Full-Spectrum Nutrition – At the heart of Nutri-Max is raw, enzyme-active bee pollen, naturally rich in B-complex vitamins, carotenoids, vitamin A precursors, quercetin, and essential fatty acids. These nutrients are critical for hormone synthesis, energy metabolism, and reproductive tissue maintenance. Bee pollen supports the HPG axis by nourishing the hypothalamus and pituitary glands, helping regulate GnRH and downstream hormone release. Its naturally occurring zinc, selenium, and magnesium also play essential roles in testosterone and estrogen production, libido, and ovarian function.
✅ Enhances Egg Quality, Yolk Nutrition & Embryo Health – Bee pollen contains high concentrations of free amino acids, phospholipids, and nucleotides, supporting the formation of healthy egg yolks and viable embryos. This translates to improved yolk nutrition, stronger shell membrane formation, and enhanced embryonic development. Its content of bioflavonoids, including kaempferol and quercetin, helps protect developing eggs and sperm from oxidative damage—improving fertility rates and supporting hatchling health from day one.
✅ Fortifies Immunity During the Breeding Cycle – Breeding birds experience immune suppression during hormone shifts, egg laying, and chick rearing. Bee pollen naturally supplies antioxidants, enzymes, and immune-stimulating polysaccharides that strengthen resistance to infection and reduce inflammation. This helps your flock stay healthy under reproductive stress and guards against opportunistic infections that could compromise breeding success.
✅ Promotes Strong Eggshells and Chick Development – Nutri-Max is enriched with natural sources of vitamin D, calcium cofactors, and vitamin K, which promote the efficient uptake and utilization of dietary calcium. This ensures strong, resilient eggshell formation, while supporting skeletal development in growing chicks. The formula also supports the absorption of trace minerals like manganese and boron, important for bone metabolism and eggshell density.
✅ 100% Natural, Safe for Long-Term Use – Nutri-Max contains no synthetic fillers, preservatives, or isolated chemical vitamins. Every nutrient is provided in its natural, food-based form, making it bioavailable and gentle on the liver and kidneys. Because it’s based on whole bee pollen and companion herbal nutrients, it is safe for continuous use during breeding seasons and beyond. Ideal for macaws, eclectus, African greys, cockatoos, and other large parrots.
✅ How to Use – Combine “Nutri-Max” (11 grams) and “HPG-Axis Boost” (40 grams) with 1 kg of bird feed and mix thoroughly. Provide this enhanced feed early in the morning, and offer fresh fruits and nuts in the afternoon.
✅ What is the Cost – Nutri-Max 1.1g per kg of bird body weight daily. A breeding pair of macaws (total weight ≈ 2.4 kg) therefore consumes 2.64g per day, meaning a 500g bag of Nutri-Max will last roughly 189 days, a daily feed cost of $0.50 per pair. Nutri-Max is used only to initiate breeding; once eggs have hatched, discontinue its use.
Buy Now - 500g $95